What if members of the armed forces could print safer weapons for use in the field? Imagine automakers using 3-D printing to produce variations of the same car while addressing different customers’ unique performance, comfort, and aesthetic preferences. While neither is quite a reality, some of the latest developments in additive manufacturing technology are expanding its applications and could become far more widespread across diverse industries. Learn what manufacturers can do with 3-D printing today.

1. Explosives
Additive manufacturing could help members of the military more precisely manipulate explosives’ internal structures to prevent accidental detonation or denotation failure. The technology enables the otherwise extremely difficult manipulation of micro-sized or nano-level layers or mixtures of explosive materials during manufacturing to produce more stable and easy-to-control weapons. The U.S. military is also researching the use of 3-D-printed explosives to create weapons on demand in conflict zones, allowing them to increase safety while avoiding shipping delays as well as unnecessary oversupply.
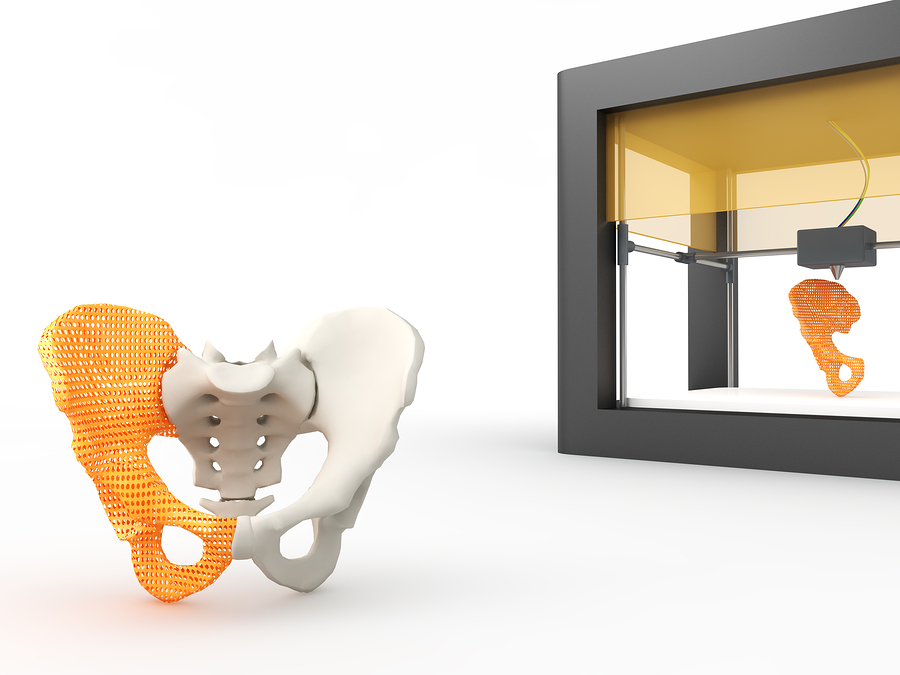
2. Prosthetics and medical devices
Rather than rely on slow manual modeling, prosthetics and medical device designers are also beginning to use 3-D printing to speed up prototyping, quickly producing models for doctors to review. Thanks to the technology, biomedical engineers can now design more personalized artificial body parts for preclinical tests based on accurate MRI scans and measurements of patients’ internal organs and physical structures. Also, addictive manufacturing is gradually proving to be the most financially viable way to make high-value medical parts for clinical trials and preliminary releases. The technology is steadily advancing toward more functional and viable biomedical part manufacturing.
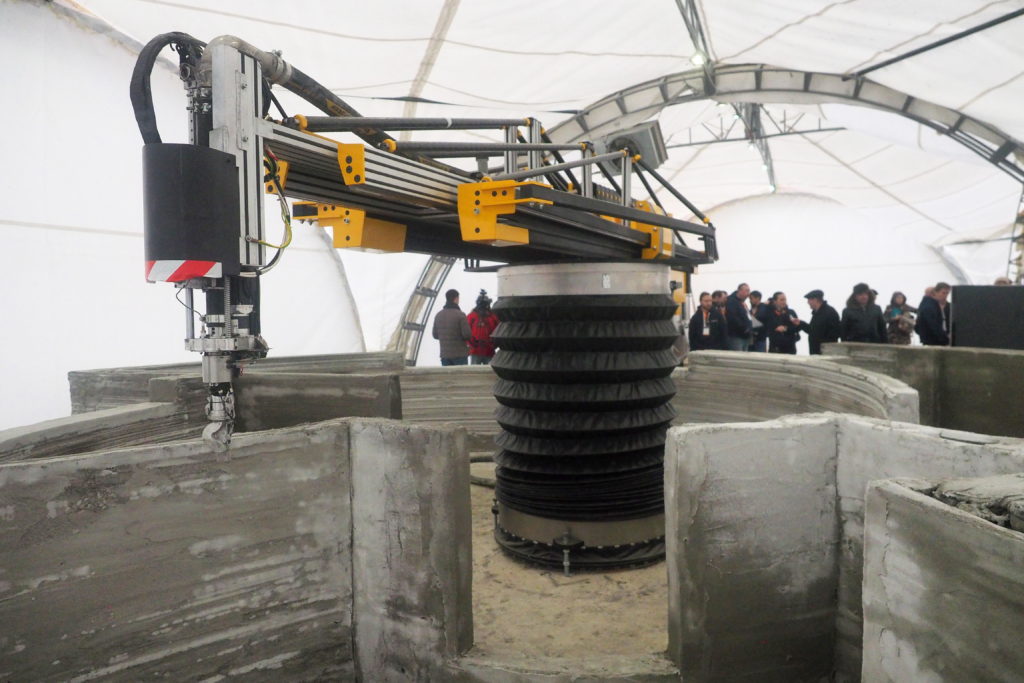

3. Homes, offices, and buildings
Due to capacity for large-scale manufacturing, 3-D printing is becoming more and more useful in megastructure construction, including bridges, houses, and offices in various parts of the world. The technology is very versatile, allowing prospective owners to build custom properties from the ground up. In the future, additive manufacturing may have an essential role in rapidly constructing small housing units to provide convenient on-demand shelter for disaster relief and for those in developing countries.
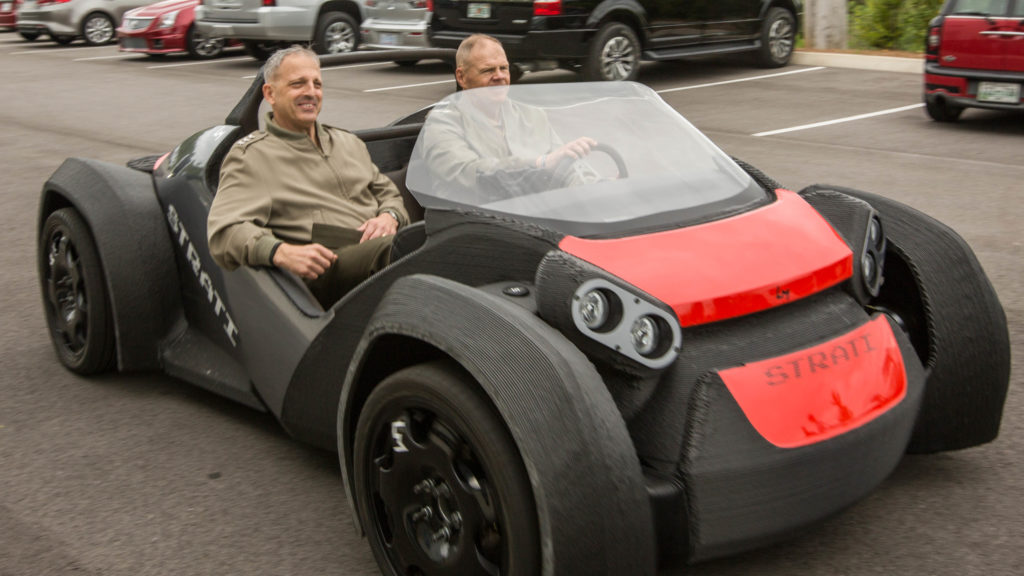

4. Cars
Automakers are also using additive manufacturing to produce vehicles. This is the case in China where manufacturers plan to introduce the world’s first 3-D-printed car in 2019. While not yet available on the market, potential buyers may directly contact the vehicle manufacturer to place their orders. Still, they may have to wait longer before they can order customized 3-D-printed cars.

5. Cosmetics and fashion
Additive manufacturing is growing far beyond industrial applications. In fact, it’s slowly gaining momentum in the fashion and cosmetics industry, especially in prototyping. While the technology is not yet ready for the large-scale profitable production of clothing and beauty products, it may form the basis for various brands to customize products according to specific on-demand consumer requirements in the future.
Today, additive manufacturing presents exciting possibilities for future advancement. While not all products are consumer-ready, you may soon see them on store shelves — or on the road.
