Rarely does a concept come around with the potential to affect change in nearly all industries. In fact, it’s argued the last innovation to achieve this was the internet itself. Today, the big buzzword is “blockchain.”
Blockchain has roots in cryptocurrency and is most widely understood as the foundation for Bitcoin. Far beyond backing decentralized currency, industry leaders are quickly realizing blockchain as a technology is a secure authentication method for everything from banking transactions to supply chain management. Now, it looks as though blockchain will break into the manufacturing realm.
The very basics of blockchain
To understand blockchain technology’s potential impact on manufacturing, we need to understand the basic premise of how it works first.
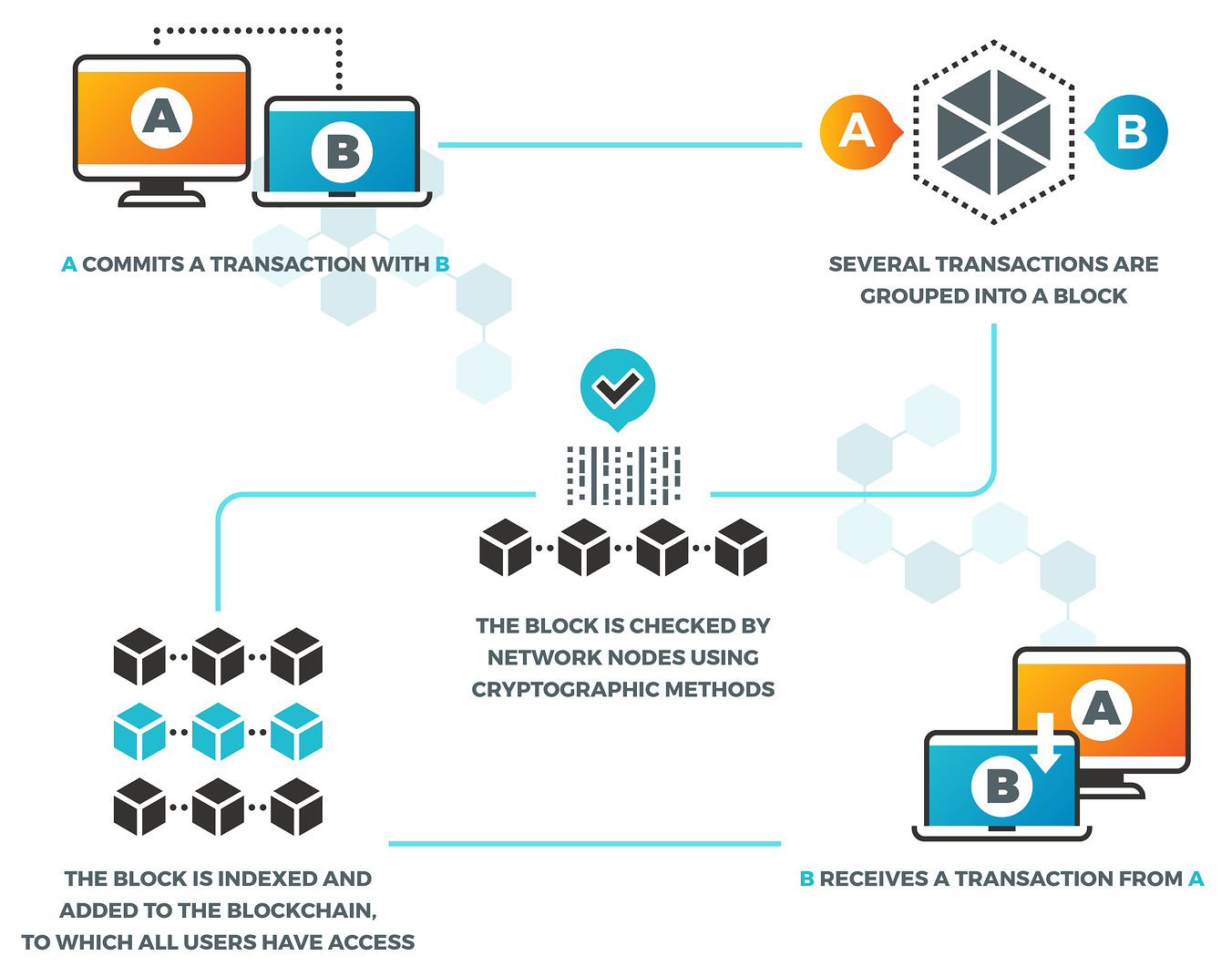
A blockchain is a ledger that doesn’t allow retroactive modification. Each entry added to the ledger, or block, links to the entry prior via a unique code. Each entry also contains a record of information publicly available to anyone with access to the blockchain. If that information is altered, so is the code, which invalidates all previous entries and shows a modification trail.
Blockchains are also decentralized, meaning peers on a network share them and everyone has a copy of the ledger. Each person recording to the ledger does so via a unique authorship key, and only someone with a valid key can add to it. In this way, they publicly maintain the blockchain, yet it remains private.
Core tenets of blockchain in manufacturing
Blockchain offers several core benefits to manufacturers in its inherent redundancy. Because the blockchain acts as an indisputable record system, it offers improvement possibilities for several key manufacturing industry areas:
- Efficiency — The peer-to-peer blockchain nature eliminates the need for manual inputs, streamlining automation in manufacturing. For example, once certain criteria are fulfilled, “smart contracts” recorded on the blockchain automatically execute transactions.
- Security — Because users can’t change blocks without invalidating the entire ledger, they can maintain strict records regarding manufacturing operations. This means maintenance supervisors cannot add to or alter the safety checks they log in the event of an accident.
- Auditability — The blockchain system of records means being able to go back ad infinitum to see records pertaining to a relevant audit. This includes the ability to check a machine’s maintenance records against warranty claims.
- Transparency — Blockchain entries are clear and unmodified, offering proof of ethics and integrity on behalf of a manufacturer. This extends to proving records of on-time deliveries to clients.
- Traceability — Block entries allow manufacturers to see exactly where materials are coming from and where finished products are going, including who’s facilitating them. They can read these block entries to trace defective parts manufacturers produce, allowing for quicker recall.
Each tenet ultimately reinforces traditional manufacturing goals: controlling, improving efficiency, creating accountability, as well as managing supply and demand.

The future of blockchain in manufacturing
Manufacturers have yet to truly realize blockchain’s impact on manufacturing, but it could come to fruition at any time. Many already recognize blockchain applications in this sector.
- Improve supply chain visibility. Creating a system of record at every handoff point in the manufacturing process could serve to cut production errors, maximize efficiency, improve accountability, and expedite operations.
- Improve transaction speeds and create transparency in the buying and selling process. Smart contracts can introduce automation to the transaction side of the business, playing on the operational automations manufacturers have already implemented. They also provide verifiable information about purchasing: What, by whom, for what price, and how much.
- Crack down on fraud and noncompliance in manufacturing operations. This also leads to better safety and improved efficacy in the work environment. Because historical records are verifiable, no way to cheat things like inspections, maintenance, and service calls exist for machinery.
Blockchain may still be best known for its role in the rise of Bitcoin, but its applications in the manufacturing sector are coming to fruition. It’s a technology rife with opportunities.